
Threat Hunting Tools: 3 Categories and 9 Notable Solutions in 2026
- 7 minutes to read
Table of Contents
What Are Threat Hunting Tools?
Threat hunting tools include Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) systems, Extended Detection and Response (XDR) solutions. Other common tools involve threat intelligence feeds, and custom scripts for specific analyses, with a range of both commercial and open-source options available.
Key categories of threat hunting tools include:
- Security information and event management (SIEM): These systems centralize log data from across an environment, allowing for correlation and analysis to detect anomalies.
- Extended detection and response (XDR): XDR provides a unified view of telemetry across various security layers, including endpoints, cloud workloads, and identity platforms.
- Threat intelligence platforms (TIPs): TIPs centralize and operationalize threat intelligence feeds, which provide up-to-date information on known threats, indicators of compromise (IoCs), and attacker tactics.
This is part of a series of articles about cyber threat intelligence.
Core Capabilities of Threat Hunting Tools
Hypothesis-Driven Investigation Support
A defining trait of threat hunting tools is their support for hypothesis-driven investigations. This approach involves formulating a theory (for example, that an attacker may be exploiting a new vulnerability or using fileless malware) and then systematically searching for corresponding indicators or behaviors.
The best tools provide structured workflows, templates, and playbooks to help analysts define, track, and test these hypotheses across diverse datasets within the environment. Hypothesis management improves hunting efficiency and performance by giving hunts a clear direction and allowing analysts to document and share their rationale and findings. Features such as task assignment, evidence capture, and dynamic note-taking are critical.
High-Fidelity Telemetry Collection
High-fidelity telemetry collection underpins all threat hunting tools as it enables visibility and deep analysis. These solutions ingest granular data from endpoints, cloud workloads, network flows, and application logs, offering detailed forensic records for every action and event. By capturing process execution traces, registry modifications, network connections, file changes, and user activity, analysts can reconstruct attack chains and uncover stealthy behaviors.
This wealth of data is only valuable if paired with efficient storage, enrichment, and indexing to enable rapid searching and contextual correlation. Threat hunting tools must therefore balance comprehensive telemetry capture with scalability and manageable data retention. Integration with EDR, NDR, and cloud log sources makes high-fidelity collection possible.
Advanced Search, Query, and Pivoting Capabilities
A central capability of threat hunting tools is the ability to perform advanced querying and rapid searching across vast datasets. Hunters need to ask complex, multi-conditional questions, such as isolating all endpoint processes launched outside standard business hours or pivoting from a suspicious domain name to related user activity.
Effective tools allow analysts to build detailed queries using flexible languages, filters, and wildcards for precision searches across logs, alerts, and network activity. Pivoting capabilities are equally important, enabling the analyst to drill down from any data point, such as an endpoint, file hash, or user account, to all recorded context across time and systems.
Context Enrichment with Threat Intelligence
Context enrichment involves bringing in external threat intelligence to illuminate raw detection data and accelerate hunting. By automatically correlating indicators such as IP addresses, hashes, and domains against threat intelligence feeds and databases, hunting tools provide instant context on whether observed activity corresponds to known malicious actors, tactics, or campaigns.
Context enrichment also supports behavioral analysis by benchmarking local activity against global threat trends. Automated tagging, enrichment, and alert validation simplify the investigation process, providing analysts with actionable intelligence without leaving the hunting console.
Related content: Read our guide to threat intelligence solutions
Key Categories of Cyber Threat Hunting Tools
Security Information and Event Management (SIEM)
1. Exabeam

Exabeam is a security operations platform with a SIEM at its core, designed to enhance threat hunting by combining data centralization with behavioral analytics and automated investigation workflows. It enables threat hunters to move from hypothesis to conclusion by providing context that goes beyond raw log data.
Key features include:
- Centralized Log Ingestion: Collects and parses data from hundreds of cloud and on-premises sources, providing a unified dataset for hunting.
- Behavioral Analytics (UEBA): Automatically baselines normal activity for every user and device, then surfaces anomalies and risky behavior that serve as starting points for a hunt.
- Automated Threat Timelines: Instead of requiring hunters to manually piece together activity, Exabeam automatically builds a chronological timeline of all user and device actions related to a potential threat.
- Advanced Search: Offers a powerful search capability that allows hunters to query vast amounts of security data to validate hypotheses and look for specific indicators of compromise (IoCs).
- Threat Intelligence Integration: Natively supports threat intelligence feeds using standards like STIX (Structured Threat Information eXpression) for formatting and TAXII (Trusted Automated eXchange of Intelligence Information) for transport. This allows for the automatic ingestion and correlation of indicators of compromise (IoCs) from commercial, open-source, and ISAC feeds, enriching event data with context about known threats and saving hunters from manual lookups.
2. Splunk Enterprise Security

Splunk Enterprise Security (ES) is a centralized threat detection and response platform that helps security teams hunt threats across hybrid environments using AI-driven detection, data visibility, and automation. Unlike traditional SIEM tools that rely heavily on predefined rules and generate high alert volumes, Splunk ES combines machine learning, user and entity behavior analytics (UEBA), and threat enrichment.
Key features include:
- Data visibility: Collects and analyzes data across all domains, devices, and cloud environments for complete context
- AI-driven detection and prioritization: Uses machine learning and AI to prioritize high-fidelity alerts and detect unknown threats
- Integrated threat hunting and investigation: Provides tools to perform ad hoc searches and structured investigations in a unified interface
- UEBA-powered behavioral analytics: Detects insider threats and anomalies by modeling user and entity behaviors
- SOAR and automation integration: Enables automated threat enrichment and incident response through prebuilt playbooks and integrations

Source: Splunk Enterprise Security
3. SolarWinds Security Event Manager

SolarWinds Security Event Manager (SEM) is a lightweight SIEM solution to improve threat detection and compliance monitoring for small to mid-sized environments. It centralizes log data from across the infrastructure, correlates security events, and enables teams to identify threats, policy violations, or suspicious activity without complex configurations.
Key features include:
- Centralized log collection and correlation: Gathers and normalizes log data from diverse sources using connectors for unified threat visibility
- Threat detection: Monitors for suspicious activity and policy violations with live cross-event correlation and alerting
- Compliance reporting: Includes out-of-the-box templates for standards like PCI DSS, HIPAA, and SOX to simplify audit preparation
- Automated incident response: Supports predefined rules and responses to reduce manual effort and improve response times
- Forensic analysis tools: Enables investigation of historical events with visualizations, filters, and saved searches
Extended Detection and Response (XDR)
4. CrowdStrike Falcon Insight XDR

CrowdStrike Falcon Insight XDR is an extended detection and response solution that delivers AI-powered threat detection, investigation, and response across endpoints. Built on CrowdStrike’s EDR foundation, Falcon Insight XDR integrates telemetry from endpoints, cloud, identity, and mobile systems to provide unified visibility and incident response.
Key features include:
- AI-powered detection and investigation: Uses Charlotte AI™ and CrowdStrike Signal to prioritize and surface the most critical threats in real time
- Real-time response (RTR): Provides direct remote access to compromised systems, enabling rapid threat containment and remediation
- Integrated XDR capabilities: Natively extends detection beyond the endpoint to identity, cloud, mobile, and data protection
- Automated threat response with SOAR: Leverages Falcon Fusion to orchestrate complex workflows and automate response actions
- MITRE ATT&CK mapping and adversary context: Enhances analyst decision-making with visibility into attacker behavior and tactics
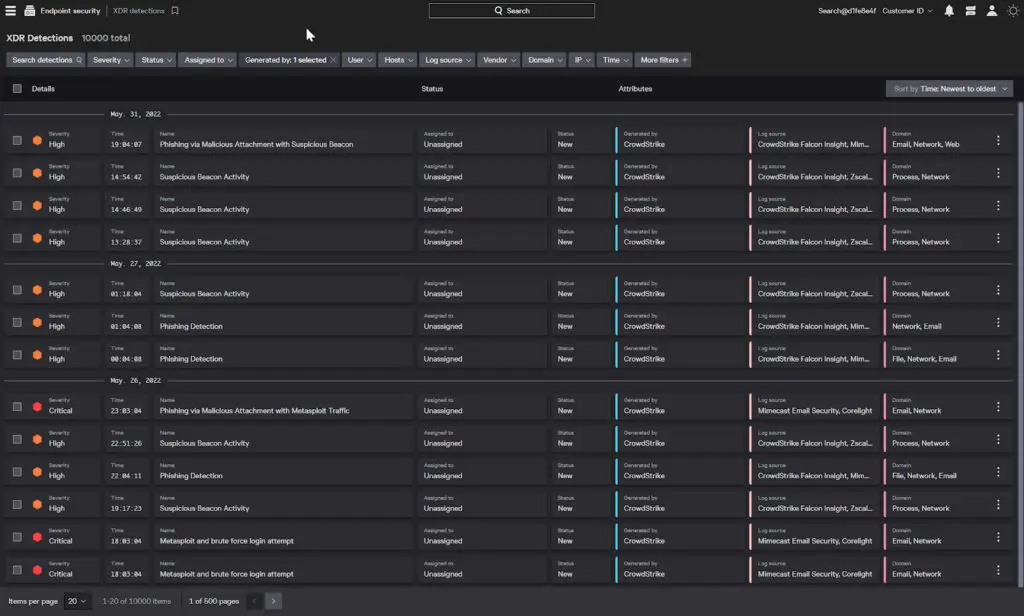
Source: CrowdStrike Falcon Insights
5. Microsoft Defender for Endpoint

Microsoft Defender for Endpoint is an enterprise endpoint security platform that helps organizations prevent, detect, investigate, and respond to threats across devices. As a component of the Microsoft Defender XDR ecosystem, it integrates natively with other Microsoft security solutions such as Intune, Defender for Identity, and Microsoft Sentinel to provide a unified security posture.
Key features include:
- Cross-platform endpoint protection: Supports major operating systems, including desktops, servers, mobile devices, and network edge components
- Attack surface reduction: Enforces security configurations and blocks access to malicious IPs, domains, and URLs to minimize risk exposure
- Endpoint detection and response (EDR): Offers visibility into endpoint activity with real-time detection, investigation, and response capabilities
- Advanced hunting: Provides a query-based tool for proactively searching threats and building custom detections using behavioral and contextual signals
- Automated investigation and remediation: Leverages automation to investigate alerts and remediate threats without manual intervention
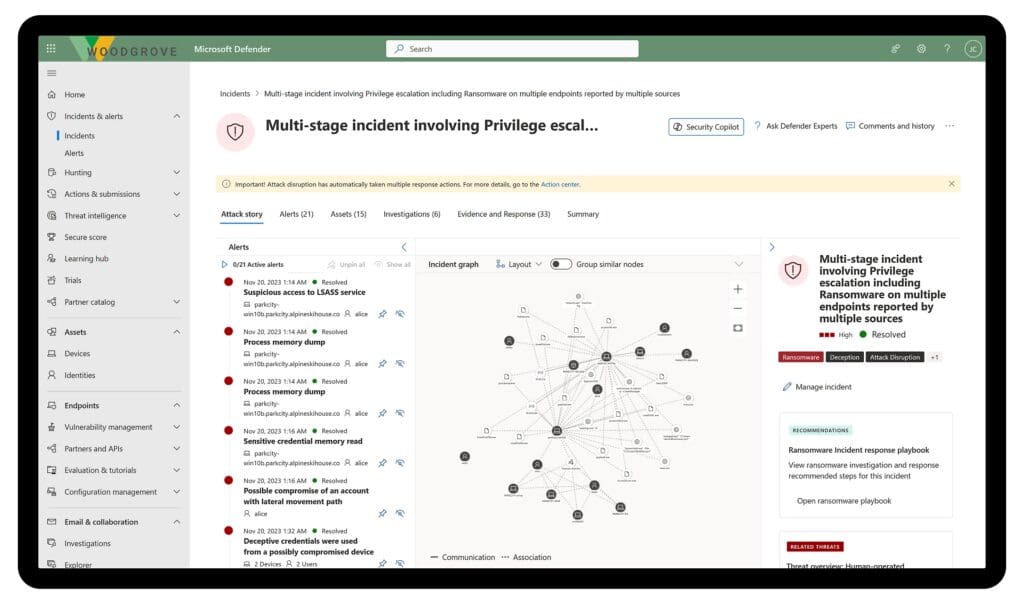
Source: Microsoft Defender
6. Cynet XDR

Cynet XDR is an extended detection and response platform that unifies security data across endpoints, networks, identities, and cloud environments to deliver visibility and faster response to threats. By consolidating multiple security layers into a single automated platform, Cynet reduces operational overhead, removes blind spots, and simplifies threat detection.
Key features include:
- Unified data collection: Gathers security telemetry from endpoints, cloud services, IAM systems, and network devices into a single platform
- Real-time threat detection: Continuously monitors connected systems and generates alerts as threats are identified
- Advanced correlation engine: Connects data points across different vectors to detect multi-stage attacks and stealthy threat behavior
- Endpoint visibility: Captures information on process execution, file changes, and system activity across endpoint devices
- IAM monitoring: Tracks suspicious user behavior, authentication anomalies, and privilege changes within identity systems like Active Directory
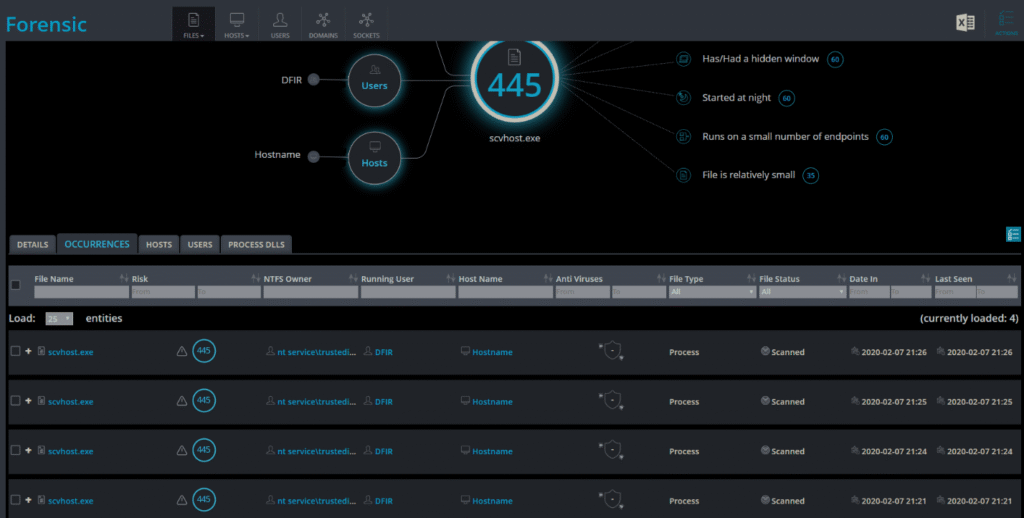
Source: Cynet XDR
Threat Intelligence Platforms (TIPs)
7. IBM X-Force

IBM X-Force is a threat intelligence and incident response organization that helps enterprises build, test, and manage security programs capable of withstanding cyber threats. Combining offensive and defensive techniques, X-Force operates as an extension of internal security teams, offering services that span threat hunting, adversary simulation, vulnerability management, and emergency response.
Key features include:
- X-Force Red Offensive Security: Conducts adversary simulations, penetration tests, and vulnerability assessments to uncover and prioritize exploitable weaknesses
- Incident response services: Provides 24/7 incident response, breach containment, and recovery support, along with readiness assessments and crisis management
- Threat intelligence services: Delivers global threat insights and intelligence-driven analysis to support risk-based decision-making and detection strategy refinement
- Cyber range exercises: Prepares business and technical teams through simulated attack scenarios that test incident response plans in a safe environment
- Adversary simulation: Mimics real-world attack techniques to evaluate detection and response capabilities under realistic threat conditions
8. Heimdal Threat-Hunting

Heimdal’s Threat-Hunting and Action Center is an integrated SIEM and XDR platform to provide visibility, behavioral analytics, and actionable insights across the IT estate. Covering endpoints, networks, cloud infrastructure, emails, and Microsoft 365 user activity, it delivers a centralized threat-hunting experience with unified monitoring and rapid response capabilities.
Key features include:
- Unified monitoring: Consolidates visibility across endpoints, cloud, networks, and users, including Microsoft 365
- Behavioral threat detection: Identifies anomalies using UEBA, Login Anomaly Detection (LAD), and email-based threat indicators to protect user identities and accounts
- Risk scoring and forensics: Delivers pre-computed risk scores and forensic data to support rapid investigation and accurate threat classification
- MITRE ATT&CK alignment: Enhances threat detection accuracy by mapping tactics and techniques to the MITRE ATT&CK framework
- Integrated Action Center: Enables one-click response actions like quarantine, scan, and isolation to simplify remediation and reduce incident response time
9. Cyble Vision

Cyble Vision is a cyber threat intelligence platform to help organizations detect, prioritize, and respond to evolving threats. By collecting intelligence from the surface, deep, and dark web, Cyble Vision provides visibility into threat actor activity, vulnerabilities, and malware campaigns. The platform leverages automation, AI-driven analytics, and real-time intelligence delivery.
Key features include:
- Multi-layer threat intelligence: Aggregates data from surface, deep, and dark web sources to detect emerging threats
- AI-driven threat analytics: Uses artificial intelligence to analyze attacker tactics, malware behavior, and vulnerabilities for faster triage
- Real-time intelligence delivery: Continuously updates threat data to support timely decision-making and automated risk mitigation
- Threat actor profiling: Offers insights into threat groups, their TTPs (tactics, techniques, and procedures), and campaigns
- Malware and ransomware monitoring: Tracks malicious payloads and infrastructure to prevent impact on critical systems
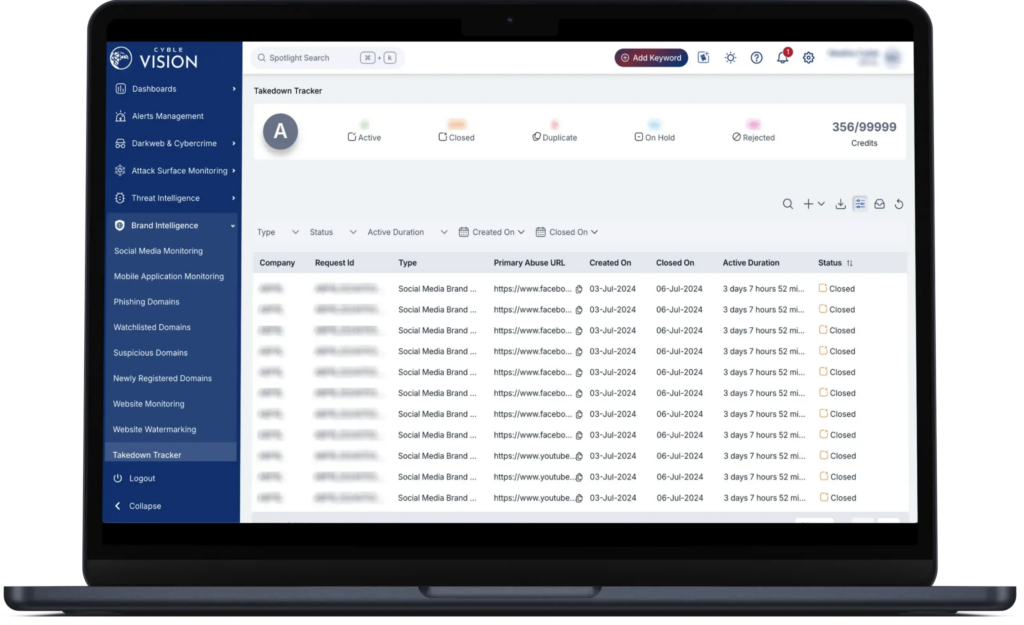
Source: Cyble Vision
Related content: Read our guide to threat intelligence platforms (comimg soon)
Conclusion
Threat hunting tools enable security teams to move beyond passive monitoring by actively uncovering threats that evade standard detection methods. By combining visibility, intelligence, and analytical depth, these tools support a proactive defense posture, allowing analysts to identify and respond to attacks before they cause significant damage.
Learn More About Exabeam
Learn about the Exabeam platform and expand your knowledge of information security with our collection of white papers, podcasts, webinars, and more.