Table of Contents
What Are SIEM Systems?
SIEM systems (Security Information and Event Management) are cybersecurity tools that centralize and analyze log and event data from various IT and operational technology (OT) sources to detect, investigate, and respond to security threats in real time.
SIEM systems combine security information management (SIM) and security event management (SEM) to provide unified security visibility, enabling organizations to identify threats, manage incidents, and meet compliance requirements. Modern SIEM solutions incorporate advanced analytics, artificial intelligence (AI), and machine learning to improve threat detection and automate responses.
How SIEM systems work:
- Data collection: SIEM systems collect security-related data, such as logs, security alerts, and events, from various sources across an organization’s IT infrastructure, including firewalls, network devices, servers, and applications.
- Data aggregation and normalization: The collected data is aggregated and normalized into a unified format for easier analysis and correlation.
- Threat detection: SIEM systems use predefined rules, correlation engines, and advanced analytics, including machine learning, to identify patterns and anomalies in the data. This process helps in detecting potential security threats and vulnerabilities.
- Alerting: When an event or pattern matches a threat signature, the SIEM generates a prioritized alert for security teams to review.
- Incident response: The system provides tools and data for security analysts to investigate alerts and manage incident response.
- Reporting: SIEM systems offer reporting and dashboards that help organizations demonstrate compliance with regulations and track historical security events.
This is part of a series of articles about SIEM tools
How SIEM Systems Work
Data Collection
SIEM solutions begin their process by collecting security event data from a vast array of sources, such as network devices, operating systems, applications, and cloud environments. This data can include system logs, authentication records, firewall logs, and alerts from intrusion detection systems.
Modern SIEMs support integration with cloud platforms and SaaS applications, extending their reach beyond traditional enterprise boundaries. The efficiency of a SIEM system is significantly influenced by the completeness and reliability of its input data. It is essential to ensure that data from all critical components are consistently collected, or gaps in visibility could occur.
Data Aggregation and Normalization
After data collection, SIEM systems aggregate information by combining log and event data from disparate sources into a unified repository. This aggregation is vital for performing correlation analysis since security incidents may span several devices and platforms. Without this centralized approach, patterns indicating a larger security event could be overlooked if data remains siloed across various systems.
Normalization follows aggregation and involves converting data into a common, structured format. Log entries from different devices may use unique terminologies or structures, which can hinder comparisons and correlations. Through normalization, SIEM platforms create a consistent schema, allowing data from varying origins to be analyzed using uniform rules and detection patterns.
Threat Detection
With normalized data, SIEM systems leverage rules, correlation engines, and increasingly, machine learning algorithms to detect threats in real time. By correlating events from multiple sources, SIEM solutions can identify sophisticated threats that may otherwise appear as isolated, benign events.
For example, a failed login attempt on a server, followed by unusual outbound network connections, could signal an active attack. Machine learning improves traditional signature- and rule-based detection by identifying anomalies deviating from established baselines. By continuously learning from historical data, SIEMs can highlight new or evolving threats that evade direct signature matches.
Alerting
Upon identifying a potential threat, SIEM systems generate alerts to notify security teams of suspicious activity. These alerts are prioritized based on severity, allowing security analysts to focus on the most critical threats first. Well-tuned SIEM platforms reduce false positives by refining detection rules and leveraging contextual information, minimizing alert fatigue.
An effective alerting mechanism is crucial for rapid threat detection and incident response. SIEMs can integrate with security orchestration, automation, and response (SOAR) platforms to automate alert triage, enrichment, and escalation processes. Automation ensures that certain types of alerts are handled instantly, freeing analysts to investigate more complex incidents and ultimately shortening response times.
Incident Response
Incident response within a SIEM system involves actions taken after the detection and verification of a security event. SIEM platforms provide workflows and playbooks to guide analysts through the steps required to contain and remediate threats. This may include isolating affected devices, collecting forensic evidence, or initiating automated countermeasures.
Advanced SIEMs often incorporate integration with other security tools, such as endpoint detection and response (EDR) products or vulnerability management systems, to enable coordinated responses. The incident response process is documented within the SIEM for auditability and improvement. After-action reviews are often performed using collected data to improve future incident handling.
Reporting
Reporting in a SIEM system delivers actionable insights and compliance documentation through structured dashboards and customizable reports. Security teams use these reports to monitor trends, measure the effectiveness of detection rules, and demonstrate regulatory adherence to leadership or auditors.
The best SIEM platforms support scheduled, ad-hoc, and compliance-specific reporting with rich visualization options. Consistent and well-designed reporting is also vital for maintaining executive awareness of the organization’s security posture. By providing visibility into key metrics such as incident response times and the volume of alerts over time, reports help justify security investments and direct efforts to areas of greatest risk.
Key Benefits of SIEM Systems
SIEM systems offer a range of benefits that improve an organization’s ability to detect, respond to, and manage security threats efficiently. By centralizing event data and enabling real-time analytics, SIEM platforms serve as a foundation for modern security operations. Key benefits include:
- Centralized visibility: SIEM platforms aggregate data from across the infrastructure, enabling security teams to monitor systems, users, and applications from a single interface.
- Real-time threat detection: Through correlation rules and anomaly detection, SIEMs can identify complex attack patterns and suspicious behavior as it happens, enabling quicker incident containment.
- Efficient incident response: Integrated workflows and automation capabilities simplify response efforts, reducing the time between detection and remediation.
- Regulatory compliance support: SIEMs help satisfy compliance requirements (e.g., PCI DSS, HIPAA, GDPR) by maintaining detailed audit logs and generating reports tailored to regulatory standards.
- Threat intelligence integration: Many SIEMs can ingest threat feeds and apply this intelligence to event data, improving detection of known malicious activity and indicators of compromise.
- Historical analysis: Retained log data enables forensic investigation of past incidents, supporting root cause analysis and continuous security improvement.
- Reduced alert fatigue: With proper tuning and contextual awareness, SIEM systems can reduce false positives, allowing analysts to focus on genuine threats.
- Scalability and flexibility: Modern SIEMs, particularly those in the cloud, scale with the organization’s needs and support diverse environments including hybrid and multi-cloud infrastructures.
Notable SIEM Systems
1. Exabeam

Exabeam is a leading provider of security information and event management (SIEM) solutions, combining UEBA, SIEM, SOAR, and TDIR to accelerate security operations. Its Security Operations platforms enables security teams to quickly detect, investigate, and respond to threats while enhancing operational efficiency.
Key features include:
- Scalable log collection and management: The open platform accelerates log onboarding by 70%, eliminating the need for advanced engineering skills while ensuring seamless log aggregation across hybrid environments.
- Behavioral analytics: Uses advanced analytics to baseline normal vs. abnormal behavior, detecting insider threats, lateral movement, and advanced attacks missed by signature-based systems. Customers report that Exabeam helps detect and respond to 90% of attacks before other vendors can catch them.
- Automated threat response: Simplifies security operations by automating incident timelines, reducing manual effort by 30%, and accelerating investigation times by 80%.
- Contextual incident investigation: Since Exabeam automates timeline creation and reduces time spent on menial tasks, it cuts the time to detect and respond to threats by over 50%. Pre-built correlation rules, anomaly detection models, and vendor integrations reduce alerts by 60%, minimizing false positives.
- SaaS and cloud-native options: Flexible deployment options provide scalability for cloud-first and hybrid environments, ensuring rapid time to value for customers. For organizations who can’t, or won’t move their SIEM to the cloud, Exabeam provides a market-leading, full featured, and self-hosted SIEM.
- Network visibility with NetMon: Delivers deep insight beyond firewalls and IDS/IPS, detecting threats like data theft and botnet activity while making investigation easier with flexible searching. Deep Packet Analytics (DPA) also builds on the NetMon Deep Packet Inspection (DPI) engine to interpret key indicators of compromise (IOCs).
2. Microsoft Sentinel

Microsoft Sentinel is a cloud-native SIEM that combines security information and event management with analytics and automation. It centralizes data from across multicloud and multiplatform environments into a cost-effective data lake, enabling faster detection, investigation, and response to threats.
Key features include:
- Cloud-native SIEM with cost-efficient data lake architecture for scalable storage and analytics
- AI-driven detection, correlation, and investigation to minimize false positives and reduce mean time to resolution (MTTR)
- Native integration with Microsoft Defender XDR for unified visibility and simplified operations
- SOAR, UEBA, and threat intelligence capabilities for comprehensive SOC functionality
- Over 350 native connectors and no-code options for broad multicloud and multiplatform data integration

Source: Microsoft
3. SentinelOne SIEM

SentinelOne SIEM, also known as the AI SIEM for the Autonomous SOC, is built on the Singularity Data Lake to deliver high-speed security. It ingests and analyzes data from sources in real time, combining AI-based detection with automated protection. It avoids indexing and schema constraints, enabling exabyte-scale performance.
Key features include:
- AI-driven detection and response that adapts to new threats in real time
- Unified console providing enterprise-wide visibility across endpoint, cloud, identity, email, and network data
- Schema-free, indexing-free design for massive scalability and faster performance than legacy SIEMs
- Support for structured and unstructured data ingestion with native OCSF compatibility
- Open ecosystem integration with first-party and third-party data, including 10GB per day free ingestion

Source: SentinelOne
4. Splunk Enterprise Security

Splunk Enterprise Security is an AI-powered SecOps platform that gives organizations visibility, fast detection, and simplified response across hybrid and multicloud environments. By centralizing threat detection, investigation, and response (TDIR) into a unified workspace, it reduces analyst fatigue and enables faster decisions.
Key features include:
- Full-fidelity visibility across domains, clouds, and devices, regardless of data location
- Centralized TDIR workflows unifying detection, investigation, and response in one platform
- Machine learning-driven UEBA for detecting insider threats, compromised accounts, and zero-day attacks
- AI-powered alert prioritization to reduce noise and focus on true positives
- SOC-wide automation and enrichment through built-in SOAR and contextual intelligence
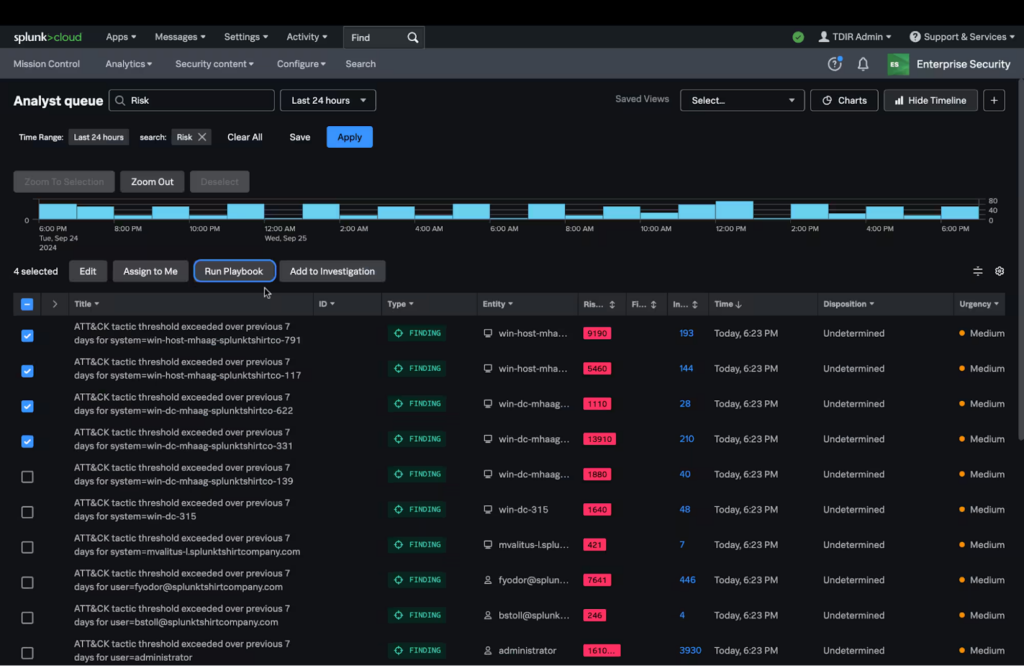
Source: Splunk
5. Rapid7

Rapid7 Incident Command is an AI-powered SIEM to unify visibility, accelerate detection, and simplify response across hybrid environments. By consolidating logs, telemetry, and asset context from endpoints, cloud, SaaS, and networks into one platform, it eliminates blind spots and delivers attack surface clarity.
Key features include:
- Unified visibility combining logs, telemetry, and asset context across cloud, SaaS, endpoints, and hybrid environments
- AI-driven behavioral analytics and UBA to detect stealthy lateral movement, privilege abuse, and anomalous access patterns
- AI-powered triage and dynamic exposure scoring to prioritize incidents by business impact and criticality
- Detection-as-code workflows for custom detection engineering and faster response to evolving threats
- Correlation of events across users, applications, and network flows to reconstruct complete attack paths with MITRE ATT&CK alignment
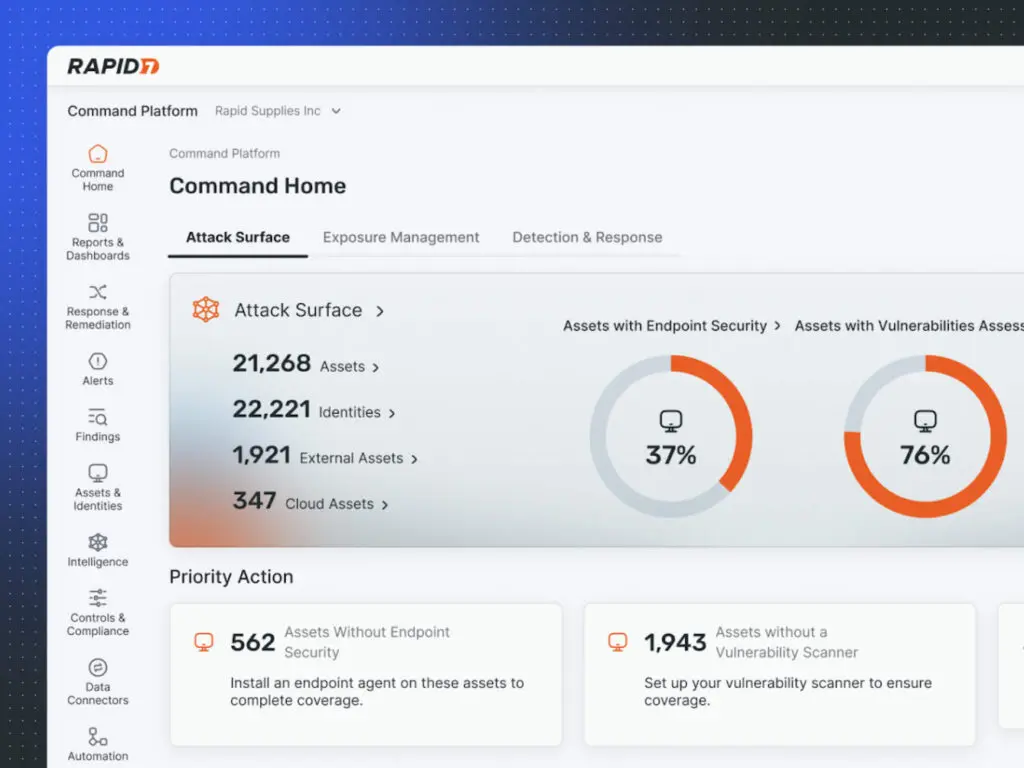
Source: Rapid7
Conclusion
SIEM systems have become a cornerstone of modern security operations, providing centralized visibility, real-time threat detection, and compliance support in increasingly complex IT environments. By aggregating and normalizing data, correlating events, and automating response workflows, they enable organizations to detect sophisticated attacks and simplify investigations. Their scalability and integration capabilities make them adaptable to hybrid and cloud infrastructures, while advanced analytics and machine learning continue to improve detection accuracy.
Learn More About Exabeam
Learn about the Exabeam platform and expand your knowledge of information security with our collection of white papers, podcasts, webinars, and more.

