Best Insider Threat Detection Tools: Top 5 in 2026
- 7 minutes to read
Table of Contents
What Are Insider Threat Tools?
Insider threat tools are security solutions to detect, prevent, and respond to risks posed by individuals within an organization who may compromise sensitive information, systems, or processes. These tools address threats from employees, contractors, trusted partners, or anyone with legitimate access to enterprise resources.
Unlike perimeter-focused security solutions, insider threat tools operate internally, leveraging monitoring and behavioral analysis to identify activities that deviate from norms. While many security frameworks target external attackers, insider threat tools fill a gap by focusing on risks that traditional solutions often overlook.
These tools integrate technologies, such as user and entity behavior analytics (ueba), data loss prevention (DLP), and endpoint monitoring to build a profile of baseline activity. When unusual patterns emerge, such as unauthorized file transfers or privilege escalations, the tools can alert security teams or automatically enforce controls, helping organizations quickly mitigate potential compromises from within.
Key Challenges in Detecting Insider Threats
Human Risk vs. Non-Human Risk
Distinguishing between human and non-human risks is a challenge in insider threat detection. Human risks originate from employees, contractors, or vendors who could misuse access either maliciously or inadvertently, complicating detection due to the trusted status of these users. Non-human risks, such as automated scripts, bots, or compromised service accounts, further blur the lines between typical and anomalous activity since they can exploit legitimate credentials to mimic workflows.
Insider threat tools must differentiate between these two categories, adapting detection logic accordingly. Automated account behavior might involve excessive data extraction or repetitive actions at odd hours, signaling an automated process rather than genuine user activity. Effective solutions cross-correlate signals from both human and non-human sources to understand intent and rapidly highlight behaviors that are out of character for a given entity.
Credential Misuse and Privilege Abuse
Credential misuse occurs when an individual uses valid account credentials outside of their intended scope, such as accessing sensitive data or systems not covered by their role. Privilege abuse is a subset where users exploit elevated permissions, for example, by copying confidential files or modifying system configurations without proper justification. Tracking such incidents is challenging due to the need to identify subtle deviations from normal access patterns while avoiding false positives that overwhelm analysts.
Insider threat tools address these challenges by baselining typical credential usage and monitoring for anomalies indicative of possible abuse. By correlating activity logs, access control changes, and system alerts, these tools help pinpoint misuse or escalation attempts in real time. Prompt detection enables security teams to step in before credentials are further exploited or damage spreads.
Data Exfiltration and Sabotage
Data exfiltration, the unauthorized transfer of sensitive information outside the organizational perimeter, is a primary concern for insider threat programs. Insiders may use various techniques to evade detection, such as encrypting files, employing external drives, or leveraging cloud storage, making traditional monitoring mechanisms less effective. Effective detection requires closely tracking data movement, analyzing context, and identifying intent.
Sabotage, including the deliberate destruction, alteration, or corruption of critical data and systems, presents a different but equally concerning challenge. Insider threat tools must differentiate between legitimate changes and malicious acts designed to disrupt business operations. They achieve this through continuous monitoring, integrity checking, and correlation of suspicious activities.
Workforce Monitoring in Hybrid Environments
Hybrid work environments complicate insider threat detection by dispersing organizational assets across on-premises and remote infrastructures. Users access sensitive resources from various locations, devices, and networks, increasing the difficulty of enforcing consistent security controls. This dispersion can mask suspicious behavior, as traditional network-centric monitoring is less effective in decentralized setups common to hybrid and remote workforces.
Insider threat tools must therefore provide comprehensive monitoring across all endpoints, cloud services, and network touchpoints. They aggregate data from diverse sources and unify visibility, allowing for behavioral analysis irrespective of physical location. By mapping activity patterns and correlating them across on-site and remote work environments, organizations can minimize blind spots, respond swiftly to emerging risks, and enforce policy adherence outside traditional perimeter defenses.
Core Capabilities of Insider Threat Detection Tools
User and Entity Behavior Analytics (UEBA)
UEBA is central to modern insider threat detection, leveraging machine learning to establish behavioral baselines for each user and entity, such as devices or service accounts. It continuously monitors interactions, looking for anomalies like unauthorized access attempts, unusual login hours, or unexpected file transfers. By comparing new activities against established patterns, ueba surfaces indicators of potential insider threats without relying solely on predefined rules or static policies.
This behavioral approach improves detection accuracy, especially for subtle or evolving attack techniques that traditional alerting would miss. ueba integrates with existing security infrastructure, ingesting logs and events from across the enterprise. It enables security operations teams to prioritize alerts, investigate suspicious activity, and adapt detection models automatically as threats and user behaviors evolve.
Data Loss Prevention (DLP) Integration
DLP solutions prevent sensitive information from leaving the organization, adding a crucial capability to insider threat tools. By monitoring content in motion, such as emails, instant messages, and data uploads, DLP can identify attempts at unauthorized data transfer. Integration with insider threat tools allows for contextual analysis, correlating content-level insights with user behavior and system events to flag risky actions more accurately.
Tight DLP integration also supports automated responses, such as quarantining files, blocking downloads, or alerting security personnel when sensitive data is at risk. By combining content inspection with activity monitoring, insider threat tools increase precision in preventing both inadvertent leaks and deliberate exfiltration.
Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) Correlation
SIEM platforms aggregate and analyze security logs and events across an organization, providing a unified view of potential incidents. When insider threat tools integrate with SIEM , they leverage this centralized data to spot threats that span multiple systems, departments, or workflows. Correlation rules help identify sequences of activity that, while benign in isolation, indicate risk when pieced together, such as accessing a database, copying files, and then attempting external transmission.
Effective SIEM-insider threat tool integrations enrich alerts with context, making investigations more efficient and actionable. Security teams gain visibility into both the granular details of individual user actions and the broader landscape of organizational risk. This enables faster triage, in-depth forensics, and comprehensive reporting.
Endpoint Monitoring and Session Recording
Endpoint monitoring enables organizations to observe user actions on desktops, laptops, and servers in real time. This includes tracking application usage, file operations, login attempts, and USB device connections. By maintaining visibility at the endpoint, insider threat tools can detect early indicators of compromise, such as unusual downloads, software installations, or unauthorized access to restricted folders, and gather evidence for potential investigations.
Session recording strengthens this capability by capturing full video or metadata logs of user sessions, enabling detailed review after an incident. Recorded sessions allow forensic teams to reconstruct the timeline of actions, understand intent, and verify whether data access or modification was in line with organizational policy.
AI-Powered Anomaly Detection
Artificial intelligence enhances insider threat tools by learning from vast streams of data and identifying patterns that might escape human analysts. AI-powered engines analyze contextual information, such as geography, device fingerprinting, recent behavioral trends, and peer-group comparisons, to surface subtle anomalies. For example, an AI model might detect a user accessing files inconsistent with their department or interacting with systems at unusual times, triggering a risk alert.
AI-driven analysis also reduces alert fatigue, flagging only those behaviors most likely to indicate true risk and filtering out irrelevant noise. As AI models adapt over time, they improve their precision based on feedback and evolving organizational behavior. This adaptive intelligence is critical for identifying advanced insider threats, including those using obfuscation tactics or novel attack vectors that bypass signature-based or rule-based detection engines.
Notable Insider Threat Detection Tools
1. Exabeam

Exabeam delivers insider threat detection as a core capability within its Security Operations platform. By combining user and entity behavior analytics (UEBA) with SIEM, Exabeam identifies abnormal behavior that signals potential credential misuse, privilege abuse, or data exfiltration before it escalates.
Key features include:
- Behavioral analytics engine: Baselines normal user and entity behavior to detect anomalies such as unusual access patterns, lateral movement, or high-risk data activity.
- Outcomes Navigator: Evaluates coverage against 16 insider and malicious insider threat use cases, identifying log source gaps and guiding teams to strengthen detection capabilities.
- Automated investigation timelines: Correlates activity across users, endpoints, and cloud systems to reconstruct incidents and speed up response.
- Integrated response automation: Connects with SOAR workflows to contain threats, revoke access, and enrich investigations with contextual intelligence.
- Flexible deployment: Available as a cloud-native or self-managed solution, supporting a wide range of operational environments and maturity levels.
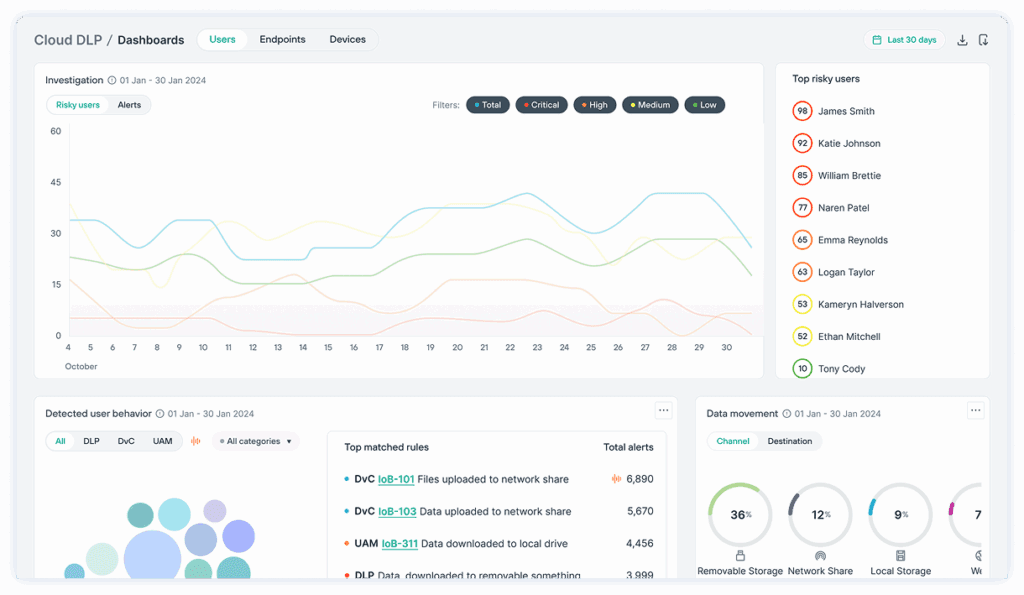
2. Forcepoint Insider Threat

Forcepoint Insider Threat is a user activity monitoring and behavior analytics solution to detect internal risks before they result in data loss. It delivers visibility into user behavior by tracking activities across endpoints, applications, and networks. The tool builds behavioral fingerprints for each user, enabling early detection of high-risk actions.
Key features include:
- Behavioral fingerprinting: Establishes individualized behavior profiles to detect deviations that may indicate malicious or negligent activity.
- Real-time user monitoring: Observes user interactions across systems to detect risky behavior as it happens.
- Automated policy enforcement: Applies security controls dynamically based on user risk level, helping prevent data theft before it occurs.
- Live video replay: Captures screen activity to provide visual context during forensic investigations.
- Sequential timelines for investigations: Presents chronological views of user actions to simplify audit and incident response.
Source: Forcepoint
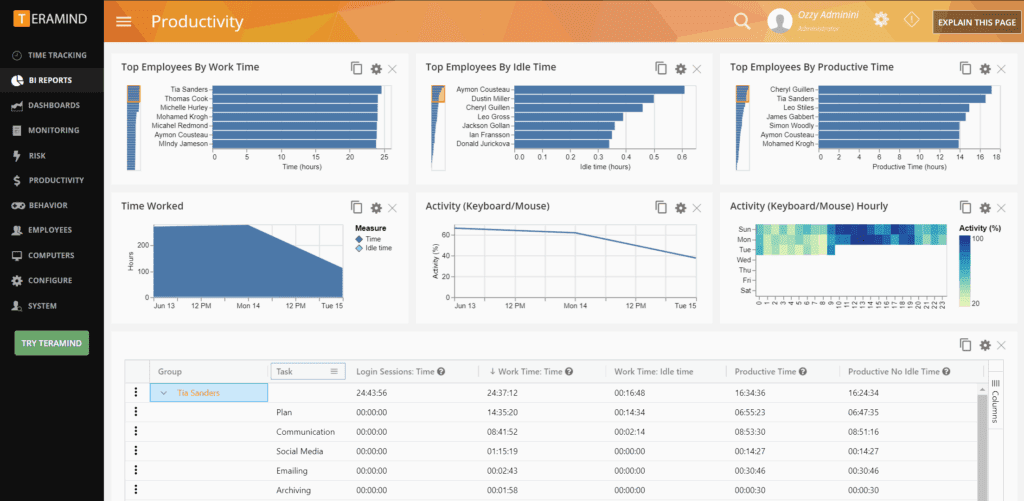
3. Teramind

Teramind is an insider threat detection platform that uses behavioral analytics and monitoring to prevent data loss, detect malicious behavior, and manage insider risk. By continuously collecting and analyzing user activity at the endpoint, Teramind provides visibility into potential threats from contractors, remote employees, and privileged users.
Key features include:
- Behavioral analytics engine: Continuously analyzes user activity to identify patterns that may indicate insider threats, policy violations, or compromised accounts.
- Activity monitoring: Tracks actions across applications, networks, and files to detect suspicious behavior as it happens, regardless of user location.
- Access control and incident response: Allows administrators to restrict or block access immediately during a security event to prevent further damage.
- Predictive risk assessment: Flags emerging risks using intelligent modeling to stop potential threats before data is exfiltrated or misused.
- Data loss prevention (DLP): Prevents unauthorized sharing, printing, or downloading of sensitive data, including HIPAA, PII, PHI, and IP.
Source: Teramind
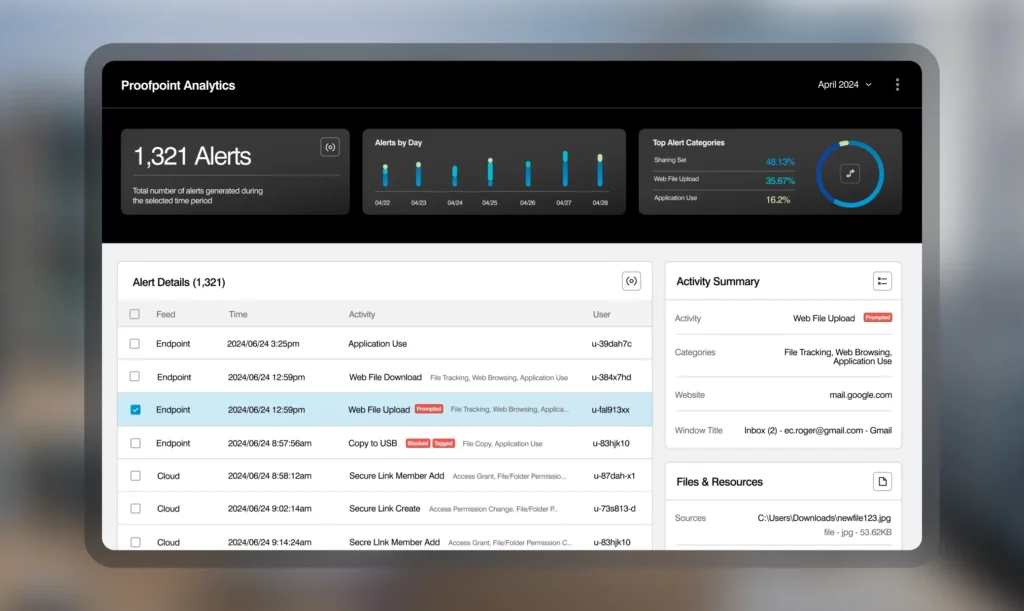
4. Proofpoint Insider Threat Management

Proofpoint Insider Threat Management (ITM) is a security solution to detect and respond to insider threats caused by careless, compromised, or malicious users. It provides visibility into user behavior across endpoints, email, and cloud applications, helping organizations reduce data loss, business disruption, and investigation time.
Key features include:
- User activity timeline: Offers a contextual view of user behavior, highlighting the who, what, when, and where of each action to support fast and accurate investigations.
- Behavioral evidence collection: Captures detailed behavioral data, including optional screenshots, to build irrefutable evidence of insider threats.
- Out-of-the-box alert library: Includes prebuilt detection rules for common insider threat scenarios, with flexibility to create custom alerts as needed.
- Multichannel visibility: Correlates telemetry from endpoints, email, and cloud services in a unified dashboard for efficient threat detection and response.
- Endpoint controls: Prevents data loss through USB, cloud sync, web uploads, and more, with risk-based controls and in-the-moment user coaching.
Source: Proofpoint
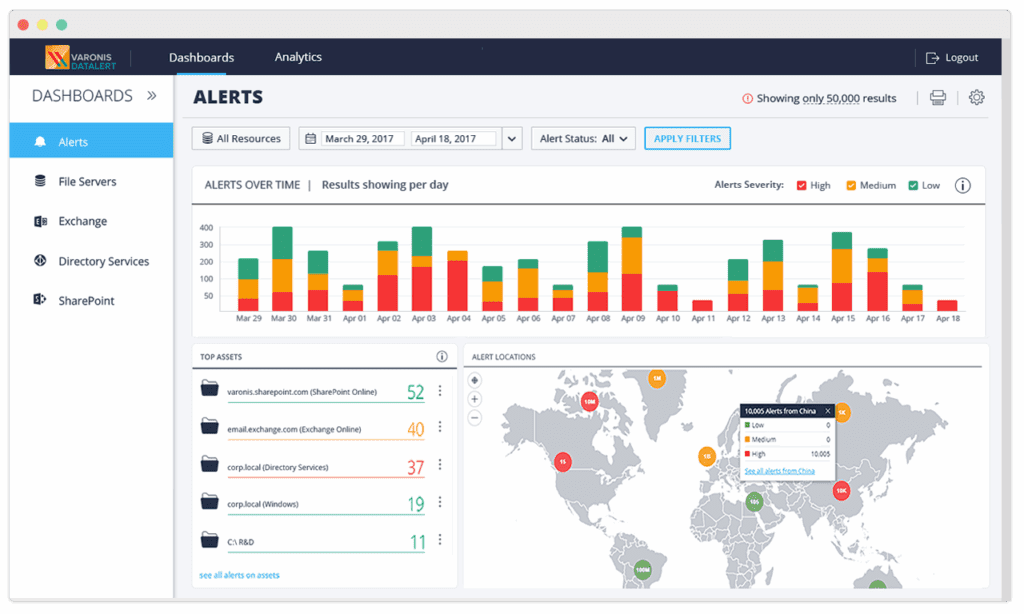
5. Varonis

Varonis Insider Risk Management is a data-centric security solution that helps organizations detect and stop insider threats before they escalate. It provides continuous monitoring, automated remediation, and behavioral threat detection to prevent unauthorized access and data exfiltration.
Key features include:
- Behavior-based threat detection: Leverages hundreds of threat models to identify anomalies in file access, permission changes, and data handling that indicate insider risk.
- Monitoring and alerts: Continuously watches for suspicious user behavior and immediately alerts security teams to threats like privilege escalation or unusual file movements.
- Automated permissions remediation: Detects over-permissioned users and automatically revokes unnecessary access to reduce the insider threat blast radius.
- Least privilege enforcement: Continuously analyzes who has access to what and automatically adjusts entitlements to maintain a least privilege model at scale.
- Data activity auditing: Tracks every access, change, and interaction with sensitive data to support incident response, compliance, and forensic investigations.
Source: Varonis
Conclusion
Insider threat detection is a critical component of modern cybersecurity strategy, addressing risks that arise from within the organization’s own perimeter. These threats can stem from negligence, compromised credentials, or malicious intent, making them particularly difficult to identify with traditional tools. Effective insider threat detection requires continuous monitoring, behavioral analysis, and the ability to correlate signals across systems and environments.
Learn More About Exabeam
Learn about the Exabeam platform and expand your knowledge of information security with our collection of white papers, podcasts, webinars, and more.
-
 Blog
Blog
Exabeam Agent Behavior Analytics: First-of-Its-Kind Behavioral Detections for AI Agents
- Show More

